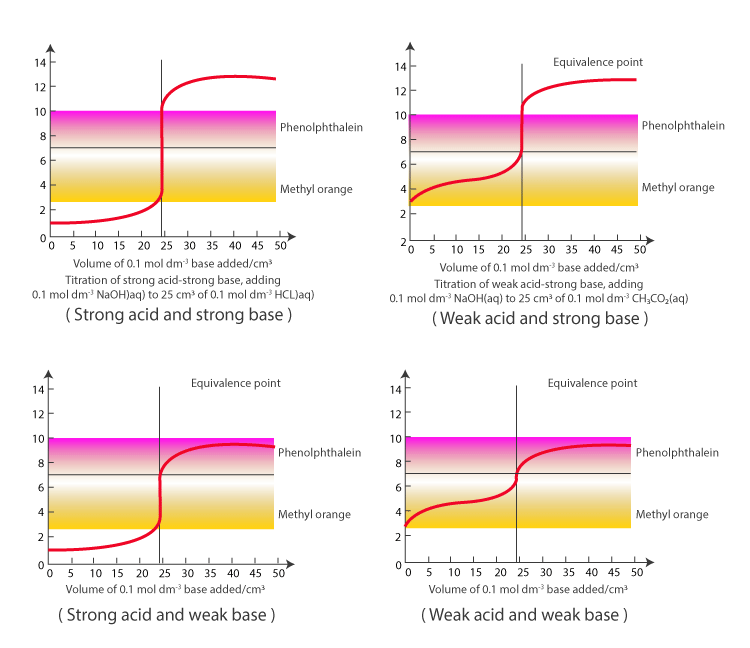
Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point . equivalence point (v = 25 ml): the equivalence point of a titration. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. In titrations of weak acids. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Explain the function of acid.
from byjus.com
Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. In titrations of weak acids. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; Explain the function of acid. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added.
Acid Base Titration Titration Curves, Equivalence Point & Indicators
Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Sorting out some confusing terms. Explain the function of acid. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; equivalence point (v = 25 ml): In titrations of weak acids. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. the equivalence point of a titration. Sorting out some confusing terms.
From www.expii.com
What Is a Titration Curve? — Overview & Parts Expii Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Consider the titration curve below for the titration of oxalic Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. In titrations of weak acids. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT How to Interpret Titration Curves PowerPoint Presentation ID225155 Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. the equivalence point of a titration. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. if the ph of an. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
15.2 AcidBase Titrations Chemistry Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): the equivalence point of a titration. Sorting out some confusing terms. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. Explain the function of. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDThe graph shows the titration curves for two Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0.. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.youtube.com
Titration curves in details. Equivalence point. Half equivalence point Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Sorting out some confusing terms. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): the equivalence point of a titration. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.youtube.com
18.3 pH curves Half equivalence point pH YouTube Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Explain the function of acid. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; the equivalence point of a titration. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. Sorting out some confusing terms. A drastic rise in ph. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDThe graph shows the titration curves for two Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Sorting out some confusing terms. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
AcidBase Titrations Chemistry Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Explain the function of acid. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. In titrations of weak acids. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; the equivalence point of a titration. . Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED ' The graph shows the titration curves for two Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Explain the function of acid. the equivalence point of a titration. In titrations of weak acids. Sorting out some confusing terms. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. postequivalence point (v. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED 2) The titration curve for the titration of a weak acid with a Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Explain the function of acid. postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. the equivalence point. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From mmerevise.co.uk
pH Curves Questions and Revision MME Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. Explain the function of acid. Sorting out some confusing terms. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. postequivalence point (v >. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From chem.libretexts.org
17.3 AcidBase Titrations Chemistry LibreTexts Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point In titrations of weak acids. the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid or a strong base occurs at ph 7.0. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. A drastic rise in ph is observed. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.youtube.com
OAT Titration Curve of Polyprotic Acids (pH = pKa1, pH = pKa2, and Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point postequivalence point (v > 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. Explain the function of acid. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From mmerevise.co.uk
pH Curves Questions and Revision MME Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Compute sample ph at important stages of a titration. In the beginning, the solution has a low ph and climbs as the strong base is added. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point of a titration. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. Explain the function of acid. . Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Using the following pH curve for the titration of a weak acid Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. Sorting out some confusing terms. equivalence point (v = 25 ml): Compute sample ph at important stages of. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From chemwiki.ucdavis.edu
Titration of a Weak Base with a Strong Acid Chemwiki Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes. Ph is determined by the amount of excess strong base titrant added; equivalence point (v = 25 ml): A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. the equivalence point of a titration.. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
From chem.libretexts.org
9.1 Overview of Titrimetry Chemistry LibreTexts Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point Explain the function of acid. if the ph of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. A drastic rise in ph is observed as the solution composition transitions from acidic to either neutral (for the strong acid sample) or basic (for. In. Ph Titration Curve Equivalence Point.